Alcohol consumption is a major public health issue in Latin America, where excessive drinking contributes to non-communicable diseases, road accidents, violence, mental health problems and economic burdens. Despite the widespread social acceptance of alcohol, the health and societal consequences have prompted governments, healthcare institutions, and advocacy organizations to implement evidence-based strategies to reduce alcohol-related harm.

Alcohol Consumption in Latin America: A Growing Concern
Alcohol consumption is particularly high in Latin America and the Caribbean. According to recent data from the World Health Organization (WHO) Global Health Observatory, the region has an annual per capita consumption of 6.5 liters of pure alcohol, making it the third highest-consuming region in the world, following Europe (10.1 liters) and North America (9.9 liters).
According to available data, alcohol consumption in Latin America has undergone significant changes between 2021 and 2024, largely influenced by the COVID-19 pandemic and the measures implemented to contain it.
During the lockdown periods in 2020, an increase in alcohol consumption was observed in some countries in the region. A survey conducted by the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) in 33 Latin American countries found that 11.2% of participants reported an increase in binge drinking from 2019 to 2020.
However, in the following years, some countries have reported a decrease in alcohol consumption. For example, in Chile, according to a World Health Organization (WHO) report published in 2024, per capita pure alcohol consumption among people over 15 years old decreased by 30% over the past decade, reaching 6.8 liters.
It is important to highlight that alcohol consumption trends vary significantly across Latin American countries, reflecting cultural, economic, and public health policy differences.
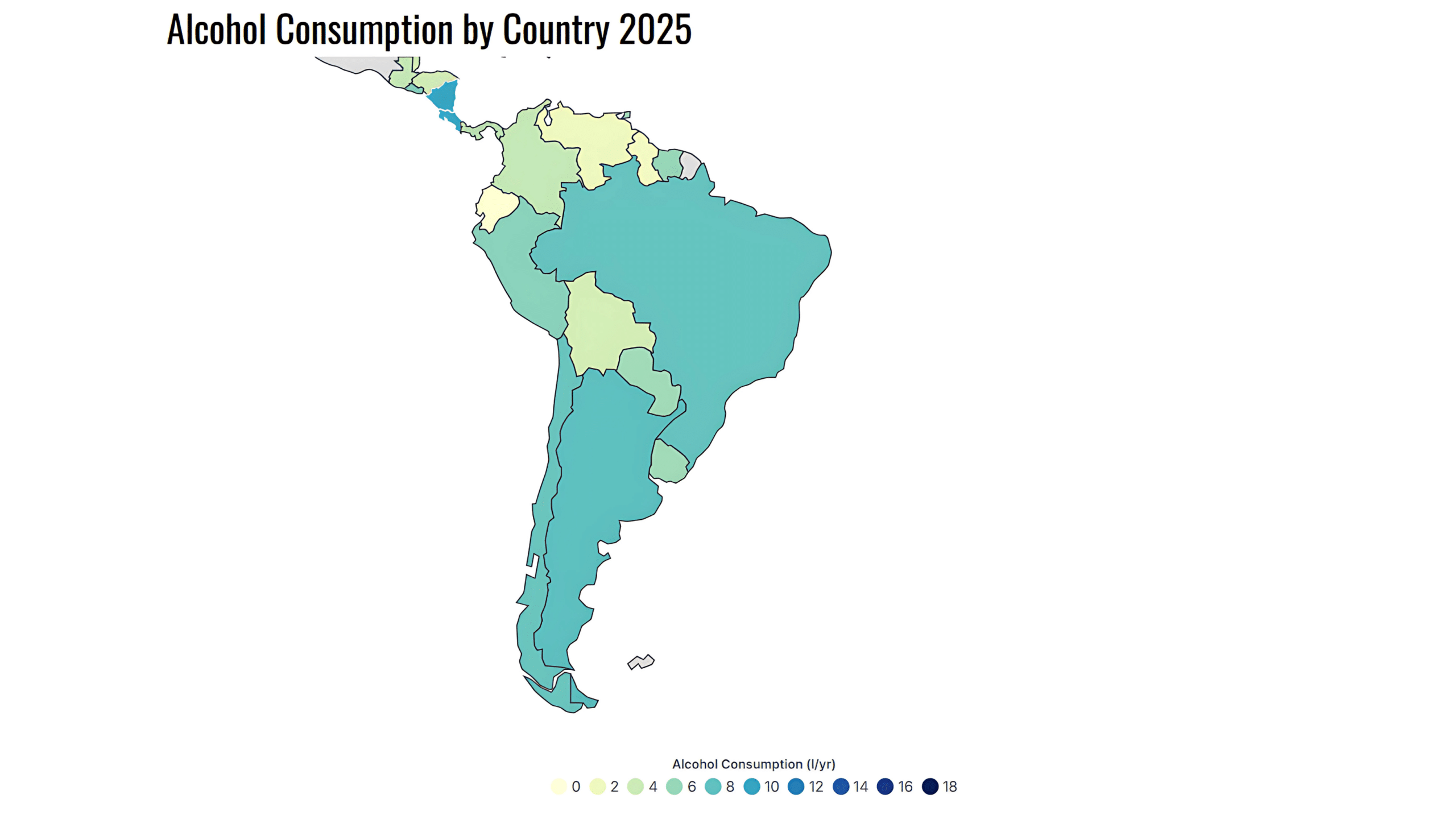
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), heavy episodic drinking (binge drinking) is particularly prevalent in the region, increasing the risk of alcohol dependence and related health complications.
Key Consequences of Alcohol Misuse in Latin America:
✔️ Increased healthcare burden due to alcohol-related diseases.
✔️ Higher rates of alcohol-impaired driving accidents.
✔️ Stronger links between alcohol, crime, and domestic violence.
✔️ Significant economic losses due to decreased productivity and absenteeism.
How Are Latin American Countries Responding?
To mitigate alcohol-related harm, WHO has launched the SAFER technical package, which can help governments reduce the harmful use of alcohol and its related health, social, and economic consequences. It includes:
- Strengthening restrictions on alcohol availability
Enacting and enforcing restrictions on the commercial or public availability of alcohol through laws, policies, and programs is an important way to reduce harmful alcohol use. - Advancing and enforcing drink-driving countermeasures
Road users impaired by alcohol have a significantly higher risk of being involved in a crash. Enacting and enforcing strong drink-driving laws and low blood alcohol concentration limits through sobriety checkpoints and random breath testing can help reduce alcohol-related traffic incidents. - Facilitating access to screening, brief interventions, and treatment
Health professionals play a crucial role in helping individuals reduce or stop drinking to lower health risks. Health services must provide effective interventions for those in need, as well as support for their families. - Enforcing bans or comprehensive restrictions on alcohol advertising, sponsorship, and promotion
Bans and comprehensive restrictions on alcohol advertising, sponsorship, and promotion are impactful and cost-effective measures. Enacting and enforcing these restrictions—especially in the digital sphere—will benefit public health and help protect children, adolescents, and abstainers from pressure to consume alcohol. - Raising alcohol prices through excise taxes and pricing policies
Alcohol taxation and pricing policies are among the most effective and cost-efficient alcohol control measures. Increasing excise taxes on alcoholic beverages has been proven to reduce harmful alcohol use while also generating government revenue to offset the economic costs associated with alcohol-related harm.
Expanding Access to Treatment and Support
One of the biggest challenges in Latin America is the limited access to alcohol cessation and treatment services, mainly due to the lack of adequate training of health professionals. To address this, various organizations are working to:
✔️ Train healthcare providers in alcohol use disorder treatment.
✔️ Expand rehabilitation and support programs.
✔️ Integrate alcohol and substance use screening into primary care settings.

ATHP: Providing Education for Healthcare Professionals
At ATHP, we recognize that healthcare professionals play a crucial role in addressing alcohol-related harm. That’s why we offer a range of free, evidence-based courses to equip professionals with the knowledge and tools needed to support individuals struggling with alcohol dependence and substance use disorders.
Key ATHP Courses Related to Alcohol and Substance Use Disorders:
📌 Prevention and Treatment of Alcohol Use Disorders
📌 Alcohol Counseling
📌 Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment (SBIRT)
📌 Substance Use and Public Health
📌 Substance Use Disorders in Primary Care
📌 Screening for Substance Use Disorders in Primary Care
📌 Mental Health and Alcohol Use: A Dual Diagnosis Approach
These courses provide healthcare providers with practical tools to screen, assess, and support patients struggling with alcohol and substance use disorders.
The Road Ahead: What More Needs to Be Done?
While progress is being made, reducing alcohol-related harm in Latin America requires continued commitment from different actors. Stronger policies, expanded treatment programs, and better education for healthcare professionals are key to long-term change. However, it is crucial to adapt treatment programs to the cultural context of each country to ensure their effectiveness and accessibility.
Are you a healthcare professional looking to enhance your ability to address alcohol and substance use disorders? Enroll in one of ATHP’s specialized training programs today and be part of the solution!
References:
- World Health Organization (WHO). (2022). Expanding Treatment for Alcohol Use Disorders in Primary Health Care. Retrieved from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/alcohol
- The WHO SAFER technical package. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241516419
- Drexel University. (2022, July). Alcohol consumption and COVID-19 in Latin America and the Caribbean. Drexel LAC. Retrieved from https://drexel.edu/lac/media/blog/2022/July/alcohol-covid19/
- World Health Organization (WHO). (2024). Global alcohol consumption trends: Chile’s reduction in alcohol intake over the last decade. Retrieved from https://aprocor.cl/2024/07/achile-disminuyo-su-consumo-de-alcohol-en-la-ultima-decada/
- Pan American Health Organization (PAHO). (2024). Workshop on alcohol taxation in Brazil, Colombia, and Mexico. Retrieved from https://www.paho.org/en/workshop-alcohol-taxation-brazil-colombia-and-mexico
